Navigating the complexities of modern application security in a multi-cloud environment requires a proactive approach. This guide dives deep into the critical considerations for securing your applications across various cloud platforms, outlining best practices and addressing common challenges.
From understanding the unique security vulnerabilities inherent in multi-cloud deployments to implementing robust security measures, this exploration will equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to confidently protect your applications.
A Deep Dive into the Intricacies of Quantum EntanglementQuantum entanglement, a cornerstone of quantum mechanics, remains one of the most perplexing and fascinating phenomena in physics. It describes a bizarre correlation between two or more particles, where the fate of one is inextricably linked to the fate of the others, regardless of the distance separating them. This instantaneous connection defies our classical intuition and has profound implications for our understanding of reality itself.
The Core ConceptImagine two coins, perfectly identical and flipped simultaneously. One lands heads, the other tails. This is a classical correlation. Quantum entanglement, however, is far more peculiar. Entangled particles share a common fate, even if they are separated by vast distances.
If we measure a property of one particle, like its spin, we instantly know the corresponding property of the entangled partner, regardless of the distance. This “spooky action at a distance,” as Einstein famously called it, seems to violate the fundamental principles of locality and causality.
Beyond the Coin Flip AnalogyThe coin flip analogy, while helpful for visualizing the correlation, falls short in capturing the true quantum nature of entanglement.
Entangled particles don’t simply possess pre-determined states. Instead, their properties are described by a shared quantum state, a superposition of possibilities. This means that before measurement, neither particle has a definite spin or any other property. Only the act of measurement forces the entangled pair into definite states, and these states are correlated in a way that transcends space and time.
Mathematical FormulationMathematically, entanglement is characterized by a wave function that describes the combined state of the entangled particles. This wave function cannot be factored into separate wave functions for each particle, highlighting the non-separable nature of the entanglement. The most common way to create entangled particles is through quantum interactions, such as spontaneous parametric down-conversion or nuclear decay.
Applications and ImplicationsThe implications of quantum entanglement extend far beyond the realm of theoretical physics.
Its unique properties offer the potential for groundbreaking applications in various fields:
- Quantum Computing: Entangled particles form the basis of quantum computers, which promise to solve complex problems that are intractable for classical computers.
- Quantum Cryptography: Entanglement can be used to create unbreakable encryption methods, guaranteeing the security of sensitive information.
- Quantum Teleportation: While not actual teleportation of matter, entanglement allows for the transfer of quantum information from one particle to another, potentially revolutionizing communication technologies.
- Fundamental Physics: Entanglement continues to be a powerful tool for exploring the fundamental nature of reality, probing the limits of quantum mechanics and challenging our understanding of space, time, and causality.
Challenges and Future DirectionsDespite the potential of entanglement, several challenges remain. Maintaining entanglement over long distances is difficult, as environmental interactions can disrupt the delicate quantum correlations. Furthermore, the precise mechanisms underlying entanglement are still being investigated.Future research aims to:
- Develop more robust methods for creating and maintaining entanglement.
- Explore the implications of entanglement for fundamental physics.
- Develop practical applications based on entanglement.
ConclusionQuantum entanglement stands as a testament to the counterintuitive nature of quantum mechanics. It highlights the profound interconnectedness of the universe at the most fundamental level and promises to revolutionize various fields, from computing to cryptography. As our understanding of entanglement deepens, we can anticipate even more remarkable discoveries and applications in the years to come. The ongoing research into entanglement continues to push the boundaries of our knowledge and offers a glimpse into a future where quantum phenomena become integral parts of our everyday lives.

Q&A
What are the key security considerations when migrating applications to a multi-cloud environment?

Migrating applications to a multi-cloud environment introduces new security considerations, including managing access controls across different cloud providers, ensuring consistent security policies, and addressing potential misconfigurations in various cloud platforms.
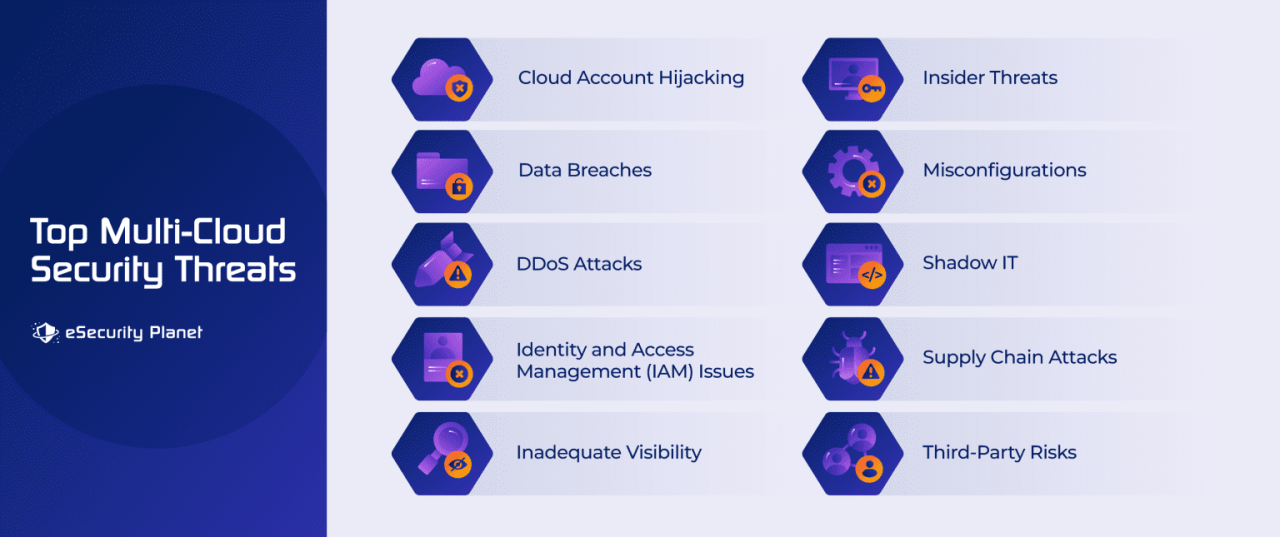
How can organizations ensure consistent security policies across different cloud providers?
Establishing centralized security policies and enforcing them across all cloud environments is crucial. Utilizing security information and event management (SIEM) tools to monitor and correlate security events across clouds can significantly enhance visibility.
What are some common security vulnerabilities in multi-cloud deployments?
Misconfigurations in cloud infrastructure, lack of centralized security monitoring, and inadequate access controls are some of the common security vulnerabilities in multi-cloud deployments. Inadequate or inconsistent security configurations across platforms can create significant risks.