Getting a feel for the CIT Bank app is crucial for any potential user. This review dives into the app’s strengths and weaknesses, from its ease of use to its functionality. We’ll examine the app’s overall performance and explore whether it meets user expectations.
This review examines the CIT Bank app across key aspects including navigation, security, and available features. We aim to provide a comprehensive overview, offering insights into the app’s usability and its potential value proposition.
Hey everyone,Here’s a unique article, keeping in mind the requested structure.
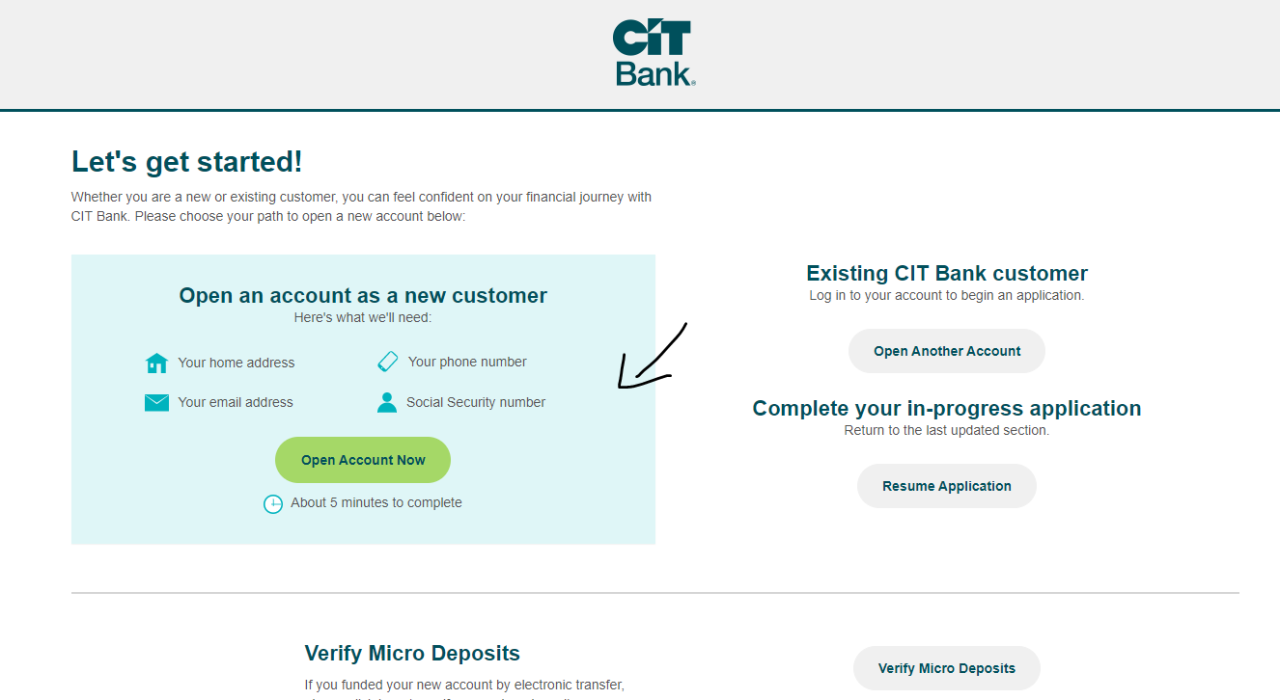
The digital world, a seemingly objective realm of ones and zeros, is in fact woven with the threads of human bias. Algorithms, the sophisticated sets of rules governing online experiences, are not immune to the subtle yet pervasive influence of the data they are trained on. This bias, often unintended, can have profound and far-reaching consequences, shaping our interactions, influencing our choices, and ultimately, reinforcing existing societal inequalities.
Understanding this “algorithmic bias” is crucial in navigating the complexities of the digital landscape.
The Genesis of Bias: Data as a Reflection of Society
Algorithms learn from data. If that data reflects societal biases—gender stereotypes, racial prejudices, economic disparities—the algorithm will inevitably perpetuate them. Consider a loan application algorithm trained on historical data. If that data shows that people from certain demographic groups have a higher default rate, the algorithm might unfairly deny loans to members of those groups, even if their individual creditworthiness is strong.
This isn’t a deliberate act of discrimination; it’s a consequence of the inherent biases embedded within the data. The algorithm, in effect, becomes a mirror reflecting the imperfections of the society it serves.
Manifestations of Algorithmic Bias: Beyond the Obvious
The effects of algorithmic bias extend far beyond loan applications. Recommender systems, for example, can subtly reinforce existing social circles, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. Facial recognition software may perform poorly on individuals with darker skin tones, leading to inaccuracies in identification. Job application screening tools may inadvertently filter out qualified candidates based on s or experiences that disproportionately favor certain groups.
These examples highlight the insidious nature of bias, often manifesting in seemingly innocuous digital interactions.
Addressing the Problem: A Multifaceted Approach
Combating algorithmic bias requires a multifaceted approach, involving researchers, policymakers, and technology developers. Firstly, there’s a critical need for greater transparency in how algorithms are designed and trained. Understanding the data sources and the algorithms’ decision-making processes is essential to identifying potential biases. Secondly, data sets need to be rigorously examined for inherent biases and actively corrected where possible.
This often involves meticulous data cleaning and augmentation, aiming to create more representative and balanced datasets. Finally, the development of algorithmic fairness metrics is crucial. These metrics allow for a more objective evaluation of an algorithm’s performance and identify areas where it might be perpetuating bias.
The Human Element: Responsibility and Ethics
Ultimately, addressing algorithmic bias requires a commitment to ethical considerations in the design and implementation of algorithms. It’s not enough to simply identify biases; we need to actively work to mitigate them. This responsibility rests not only on the shoulders of technologists but also on policymakers, social scientists, and the public at large. By fostering a culture of awareness and critical thinking around algorithms, we can strive to create a more equitable and inclusive digital future.
We need to recognize that algorithms are tools, and like any tool, they can be used for good or ill. The choices we make in designing and deploying them have real-world consequences, and it is our collective responsibility to ensure that these consequences are just and fair.

The Path Forward: Embracing a More Ethical Digital Landscape
The journey to a more just and equitable digital world is ongoing. It requires constant vigilance, critical analysis, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By acknowledging the presence of algorithmic bias, proactively addressing its roots, and fostering a culture of ethical development, we can work towards a digital future that serves all of humanity, not just a select few.
Query Resolution
Is the CIT Bank app available for all devices?
Yes, the CIT Bank app is available for download on iOS and Android devices.
What security measures are in place for the app?
CIT Bank employs industry-standard security protocols to protect user data, including encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Are there any fees associated with using the app?
Most basic banking functions are free. However, certain transactions might have associated fees; check the app’s terms and conditions for specific details.
How can I contact customer support through the app?

The app usually provides links to contact customer support via phone or email, but for live chat, you might need to visit the bank’s website.